Automated email communication protection
machine-to-human emails
We believe in effective cyber security protection by providing humans easy and interpretation-free ways to decide and therefore avoid risks related to cyber attacks and risk-awareness.
Cyber risks not only are a threat by themselves, they also create decision-blockage situations on professionals that are aware of risks but lack proper protection tools.
"PROTECT YOUR BRAND AND YOUR COMMUNICATIONS WITH CUSTOMERS BY ALLOWING A TRUSTFULL EMAIL VERIFICATION"
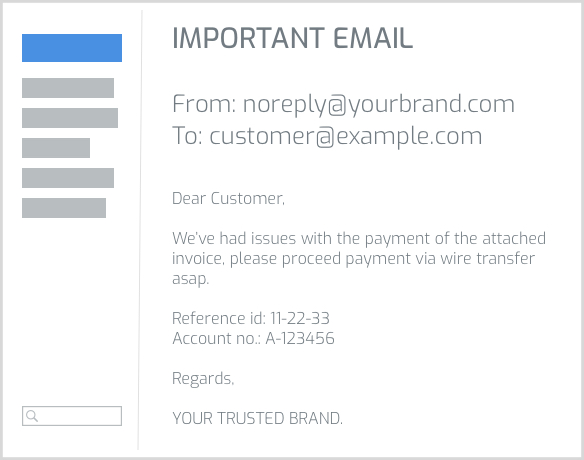
FACTS ABOUT OUTBOUND PHISHING AND BRAND SPOOFING:
There's no way you can't avoid cyber attackers using your brand in their attack strategies.
What you can do is provide anyone that might receive an email from you an easy and interpretation-free mechanism to verify its authenticity.
That's what Zuratrust does, provide an easy way to detect & avoid fake emails.
Request a Demo
Main features
Other features
corporate email platforms
personal email platforms
with emails sent and received
in all kinds of devices
Machine-to-human
automated emails protection
Protection for automated email communications from any business-application (transactional or non transactional) to end users such as customers, suppliers or even employees.
According to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (www.IC3.gov is an entity within the USA Department Of Justice and the FBI whose mission is to gather complaints and data on cyber attacks) 91% of cyber attacks use "emails" sent to humans as the #1 attack vector. This percentage is increasing overtime.
Why should you protect all your email communications?
Current cyber attacks rarely attack infrastructure or hardware resources, they focus their efforts in the less protected and much more error prone Human Factor as their preferred target.
And it really doesn't matter what kind of cyber-attack we might analyze or whichever might be the final objective of the attacks, we'll find the same common patterns and strategies, they all execute the attack using fake emails impersonating people or entities the victim knows and trusts.
RANSOMWARE
- Ransomware in Wikipedia -Probably the cyber attack with most media coverage among all. Wannacry, Petya, CryptoLocker, CryptoWall and many other variants might be names you've already heard on news.
This attack technique encrypts all your data in notebooks, workstations, servers, NAS storage appliances and also in connected cloud storage services your might be using as file sharing or even as backup. Victims are requested a ransom (commonly in cryptocurrencies like bitcoin) in order to recover data and regain access to business applications. It is easy to find organisations that currently are or have suffered the effects of this threat, and losses are not only related to the ransom itself, production and business downtime during the minimum of two to three weeks time to be back partially operational might be a period your organisations will not be able to recover from (in addition to data loss, conficence issues and so on). Falsified email messages are the most common attack tool when executing this attacks.
OUTBOUND PHISHING
- Ransomware info in Wikipedia -This type of cyber attack is probably the most widely spread around the world targeting big organisations that own very recognized and trustful brands as well as public institutions and government agencies. An Outbound Phishing attack uses the aforementioned trustfulness of the organisations brand and sends impersonated emails to potential customers as if they're sent from the brand itself. Commonly the recipients of the emails are encouraged to pay an invoice, provide access credentials or even send business and personal information.
IT & OT NETWORK INTRUSSION
- Why phishing remains a critical cyber-attack vector -"It is easier and much more cost effective to trick a human to perform an operation that might allow a remote attacker internal network access than it is to search and exploit a vulnerability in network infrastructure or hadware/software solutions."
That's what we can infer from cyber gangs activity. One of the top strategy deployed in this attacks are well prepared and crafted fully credible emails humans will trust and might never get to know were an attack. Knowing which emails are real and were indeed sent from its alegged sender becomes key when protecting organisation and its human capital from all kinds of cyber attacks.
CEO FRAUD
- Email Fraud and CEO Fraud in Wikipedia -- BEC, The 12 Billion Dollar scam by FBI-iC3.gov -
Also known as BEC or Business Email Compromise, CEO Fraud attacks impersonate email communications between offices of your own organisation, customers, suppliers, banks or even tax agencies to drive attacked victims to perform fraudulent wire transfers to any compromised bank account all over the world. Highly skilled cyber gangs with huge resources have made this attacks a very profitable business costing billions of dollars to companies around the world (2 out of every 10 attack attempts are said to be succesfull). Other variants also perform step-by-step information escalations involving phone number or bank account information modifications in your informations systems (ERP, CRM,...) in order to get the money of future payments and to avoid internal protection mechanisms.
Both the incidence and losses related to this attacks are growing exponentially all over the world targeting organisations from all sizes and activities.
GEOPOLITICAL
DISESTABILISATION
- Emmanuel Macron email leaks linked to Russian-backed hackers who attacked Democratic National Committee -Several countries and democratic election processes have suffered the effect of this attacks in recent years and the use and incidence of geopolitical disestabilization and intromission strategies is expected to grow widely in the following years. From the United States to France, many countries have suffered the effects of leaking cherry picked email communications with private or political information of campaign members or candidates to the public and its effect on the public oppinion.
INDUSTRIAL AND MARKET
KNOW HOW THEFT
- Symantec 2019 Internet Security Threat Report -When an attack ends with a money transaction is much easier to detect and assess the loss, but when it is related with information, know how, technical data or the output of years and years of product Research and Development the alarms don't sound as clear.
Most of the time the organisation will never know the attack even happened, although suspicions might arise when the competition launches it's new flagship product to the market mimicking the state of the art of an innovative technology your company developed after huge efforts.
CYBERSECURITY IS THE JOURNEY AND NOT A DESTINATION
Current cyber attacks rarely attack infrastructure or hardware resources, they focus their efforts in the less protected and much more error prone Human Factor as their preferred target. And it really doesn't matter what kind of cyber-attack we might analyze or whichever might be the final objective of the attacks, we'll find the same common patterns and strategies in mostly all of them. Protecting your organisation and your email communications from all kinds of attacks will make you a less cost effective target for cyber gangs, although we all know (or at least we should) that cyber security is a journey that drives resilience and will never be a destination we'll reach one day.
